Look at key events, concepts, terms, quotes or phenomena every day and brush up on your knowledge. Here is today’s UPSC Current Affairs knowledge nugget on India’s heaviest telecom satellite.
(Relevance: Space technology forms an important part of the UPSC CSE curriculum. From time to time, UPSC asks questions on various space missions and launch vehicles. Hence, it becomes important to know the missions in the news.)
Why in the news?
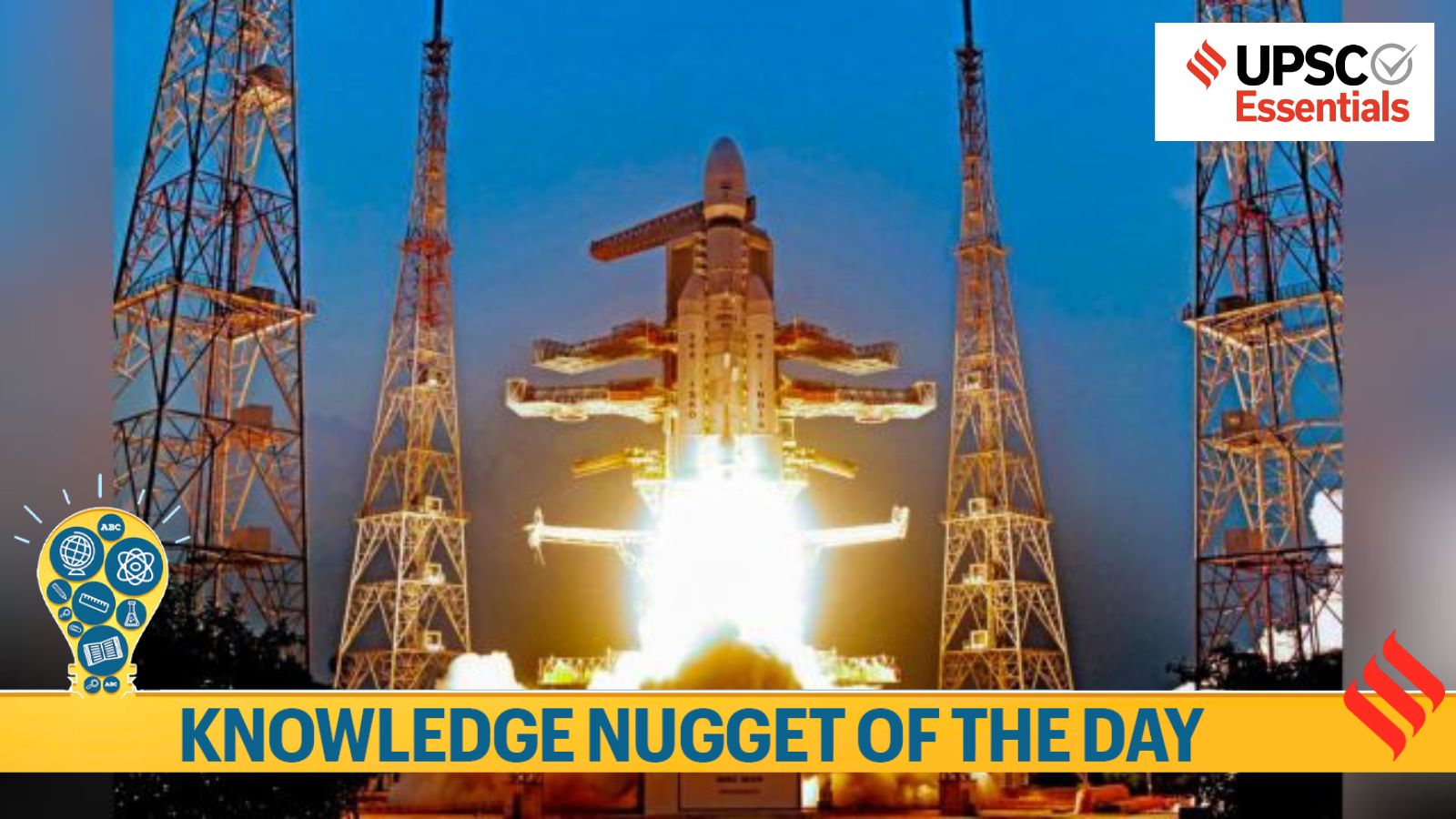
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) successfully completed the launch LVM3-M5, Breaking another record by launching the heaviest communications satellite from Indian territory, CMS-03. Since it is a showcase of ISRO’s steadily improving capabilities, let us learn about it in detail to understand its importance.
Key takeaways:
1. The launch of LVM3-M5 marks the first time that ISRO has placed a communications satellite weighing more than 4,000 kg in a remote geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) from Indian territory.
2. The payload, CMS-03, is a multi-band communications satellite weighing 4,410 kg. It is a multi-band communications satellite that will provide services across a wide oceanic area, including the Indian landmass. It is designed to provide services for at least 15 years.
3. Also known as GSAT-7R, CMS-03 is a replacement for the GSAT-7 satellite, launched in 2013 on an Ariane-5 rocket, which has reached the end of its life.
4. The satellite will primarily serve the purposes of the Indian Navy, augmenting its satellite communications and maritime domain awareness capabilities.
Story continues below this ad
5. “GSAT-7R will provide robust communications coverage across the Indian Ocean region. Its payload includes transceivers capable of supporting voice, data and video links across multiple communications bands. This satellite will significantly enhance connectivity with high-capacity bandwidth, enabling seamless and secure communication links between ships, aircraft, submarines and maritime operations centers of the Indian Navy,” a MoD statement said.
6. It is worth noting that ISRO has launched a heavier satellite than this. The GSAT-11 missile launched in 2018 weighed more than 5,800 kg but used the European Ariane-5 missile. The Indian Space Research Organization was relying on the European rocket to send all its heavier satellites, which weigh more than 3,000 kg.
7. With CMS-03, ISRO demonstrated the LVM3 missile’s ability to lift heavy weights. Thus, the launch of LVM3-M5 is an important step towards reducing foreign dependence on space programs and lowering the costs of upcoming missions. It is also evidence of ISRO’s growing strategic independence and technological independence in carrying out increasingly complex missions.
Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3)
8. the lvm3, Formerly GSLV Mk-3It is ISRO’s most powerful missile. It is capable of carrying up to 8,000 kg to low Earth orbit and 4,000 kg to geosynchronous orbit.
Story continues below this ad
9. LVM3 uses a combination of solid, liquid and cryogenic engines and has already launched major missions such as the Chandrayaan-2, Chandrayaan-3 and OneWeb satellites. For this mission, the target orbit was lower (about 29,970 km at the highest point) to accommodate the heavier satellite.
10. ISRO has modified the rocket to increase its payload capacity by 10 per cent compared to the previous launch LVM3 (LVM3-M4) carrying Chandrayaan 3. The vehicle has been named “Baahubali” for its weight capacity. The vehicle’s cryogenic upper stage was upgraded from a C25 (carrying 28,000 kg of fuel and generating 20 tons of thrust) to a more powerful C32 stage (carrying 32,000 kg of fuel and producing 22 tons of thrust).
Behind the block: ISRO launch vehicles
1. Satellites do not go into space on their own. They would have to be transported there by launch vehicles, or rockets, such as the PSLV. Rockets have powerful propulsion systems that generate the huge amount of energy needed to lift heavy objects such as satellites into space, overcoming Earth’s gravity.

2. ISRO Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) It is a three-stage launch vehicle with three stages of solid propulsion. It also has a fluid thrust-based speed reduction unit (VTM) as a final stage, which can help adjust speed as it prepares for satellite placement.
Story continues below this ad
3. No Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) It is the third generation of Indian satellite launch vehicles. It was first used in 1994. More than 50 successful PSLV launches have been conducted so far. It has also been called the ‘backbone of ISRO’ for continuously delivering various satellites to low Earth orbits (at an altitude of less than 2000 km) with a high success rate.
4. Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicles (GSLVs) It was instrumental in launching communications satellites into geosynchronous transfer orbit. According to the European Space Agency (ESA), communications satellites are typically placed in geostationary Earth orbit (GEO). It is a circular orbit at an altitude of 35,786 kilometers above the Earth’s equator.
5. GSLVs have higher power because sending satellites deeper into space requires more energy. Therefore, cryogenic engines consisting of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen are used in GSLVs because they provide greater thrust than engines used in older launch vehicles.
Post a reading question
Referring to Indian satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2018)
Story continues below this ad
1. PSLVs launch satellites useful for monitoring Earth’s resources while GSLVs are primarily designed to launch communication satellites.
2. Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
3. GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle, the first and third stages use solid rocket motors; The second and fourth stages use liquid rocket engines.
Which of the above statements is true/correct?
(A) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 3 only
(Sources: Five things to know about LVM3-M5, ISRO launches heaviest satellite from India in show of growing strategic independence)
Story continues below this ad
Subscribe to our website UPSC Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – Indian Express UPSC Hub, follow us Instagram And X.
🚨 Click here To read UPSC Essentials Magazine October 2025. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or on @manas.srivastavaindianexpress.com🚨
(Tags for translation)India’s heaviest communication satellite